
Many infections cause no symptoms in healthy people. The immune system suppresses the virus activity, thus a person becomes a carrier of infection. When this transfer of the pathogen to other people even when full clinical well-being, because the viral particles are contained in the biological fluids of a patient. Hidden during infection may be the underlying cause of a significant spread of the disease: patients in a timely manner do not pass the survey and continued to infect other people irresponsible.
Papilloma virus (HPV), can be called a great example of hidden infectious agent. Most people are infected with at least one type of HPV throughout life, however, the clinical manifestations of the disease occur far not in all cases. For distance complications of infection doctors include an increased risk of developing a malignant tumor. When it in patients who suffer from immunodeficiency, often arises such a negative consequence of the disease. Current drugs help suppress the symptoms of HPV infection. It is also recommended to timely vaccination.
Read more about the disease and
The Virus hpv is the causative agent of infection that affects the skin and mucous membranes of the organs. The main manifestation of the disease is the growth of tumors in the facial area, genitals, mouth and throat. In some cases, genital papilloma consists in non-specific places, like the skin of the lower and upper limbs. Localization of warts depends on the type of HPV. For most people, injection leads to the overt carriage of the infection, but in the reduction of immunity, the virus begins to manifest its virulence. In some cases, immunocompetent cells alone destroys the pathogen within 3-6 months after its infestation in the body.
HPV infection is the most common disease transmitted sexually. This indication can be explained by the high virulenceYu of the virus and asymptomatic in the course of the pathology in the majority of people. The use of condoms not always allows to prevent infection, so the patient can continue to distribute the virus even when protected sexual contacts. At the same time, experts have developed effective vaccines to prevent the development of the oncogenic forms of HPV. Immunization is indicated for girls in their teens, because protection against the virus is necessary to instill into the first sexual intercourse.
Properties of the virus
The Virus hpv is a DNA containing patogenom. Unlike bacteria and other micro-organisms, viruses can carry out their activities only after the introduction into a cell and insert their own genetic information in the nucleus. Thereafter, the affected cell begins to synthesize protein, required for assembly of viral particles. Almost all representatives of the family of human is attacking only one kind of organisms, while HPV infection can only occur in humans.
Scientists know of over 600 species (types) of the virus hpv, which differ in genetic information. 40 types of HPV cause different forms of lesions of the mucous membranes and skin. In this crucial clinical importance is the classification of extent oncogenetic strains. So, cancer of the cervix in women most often arises in the assault of HPV 16 and 18 types. These infectious agents do not always manifest themselves by skin changes.
HPV affects the base layer of the epithelium. The pathogen can exist in the form of episome, is not associated with the cellular DNA, or integrated forms, related to the genome of the cell. This is the reason the integrated virus producing the necessary proteins and causes the clinical manifestations of the disease. The activity of HPV in our body, is the immediate cause of malignant degeneration of the tissues, but the carriage of the virus increases the risk of cancer risk factors.
Methods of infection
The Virus is contained in the basal cells of the epithelium, so that no microtrauma of the skin and mucous membranes, increase the risk of infection. In most cases, HPV is transmitted during vaginal, anal, or oral sexual contact. A condom can be secured only part of the surface of the skin, but viral particles can penetrate into the body through the other veils. The presence of genital warts predisposes to the transmission of the pathogen, but outwardly intact skin of the wearer of the disease is also a source of HPV.
Other transfer methods
- Injection baby during childbirth. In children the most commonly encountered lesions of the respiratory tract
- Separate transmission of the virus from one part of the body on the other
- The total use of personal items, including razors, toothbrushes and towels
- The blood transfusion. Recent studies have confirmed the possibility of transfusion infection.
- Surgical procedures in non-sterile conditions
Despite the different causes of viral infection, only the sexual method of contracting HPV has clinical significance. Other sources of infection are characterized by a low risk of spread of the pathogen.
Risk factors
In addition to direct routes of transmission of HPV, it is necessary to also consider the role of risk factors. It is about the specifics of the individual lifestyle and particular physical states.
The key factors of the risk of infection
- A large number of sexual partners. Even when safe sex active sex life sooner or later leads to disease.
- Age. Genital warts in most cases identified in adolescents and young patients, while the warts of the oral cavity and respiratory system are typical for children.
- A weakened immune system. Patients who suffer from HIV or acquired immunodeficiency, are at high risk of viral infection. Also, HPV often manifests itself symptomatically after organ transplantation.
- Damage to the skin and mucous membranes. Microtrauma facilitate the penetration of the virus in the base layer of the epithelium.
- Smoking and alcoholism. Bad habits weaken the activity of the immunity.
- Infections of the urinary infection.
In addition, the group risk of infection include pregnant women. It must be remembered that the removal of the factors of predisposition to the disease, is an effective preventive tactics.
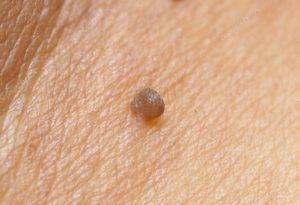
Clinical time
The incubation period preceding symptomatic manifestations of the disease, may persist for several months or not. In immunocompetent patients in that time, the body can destroy the infection, however, spontaneous elimination of the pathogen is not always happening. A person can be simultaneously infected with multiple strains of the virus. Symptoms of HPV infection arise when the influence of unfavorable factors, debilitating the immune protection of the tissues. Due to the repetitive stream of the warts regularly disappearing and forming again. Cancer complications of the infection may develop in the course of a few decades.
Possible consequences of the disease:
- Cervical cancer – a malignant tumor of the epithelial tissue. This kind of oncology associated only with the hpv virus. When early vaccination is the risk of oncogenesis reduces.
- Squamous cell carcinoma of the anal opening. Such complications can occur in both men and women. Early symptoms of cancer of the anus include bleeding and itching of the skin.
- Violation of urination due to obstruction of the urethra warts.
- Malignant degeneration of warts in the throat and oral cavity.
Cervical cancer is one of the most common causes of death among women. Because this disease is caused by virus invasion, it is necessary for regular completion of examination at the gynecologist. Modern vaccines protect women from the most oncogenic types of HPV.
Diagnosis
A survey of warts is engaged gynecologists, urologists, venereologists and dermatologists. In the course of the primary reception the doctor asks the patient about the complaints, collect the anamnestic data and performs a physical examination of the skin manifestations. Usually manifestations of the HPV easily identified, however, it is necessary to exclude other disease. For this the specialist will prescribe the instrumental and laboratory research.
The necessary methods of diagnostics:
- Instrumental examination of the vagina and cervix (colposcopy). Such a survey necessarily performed for cervical cancer screening. During the examination the doctor can detect multiple papilloma and lands epithelial dysplasia.
- Biopsy – obtaining a fabric material in the area of the skin or mucus changes. Cytological studies of the sample allows to detect malignant cells.
- Polymerase chain reaction – detection of viral particles of HPV in the body. The course of this test gives doctors the opportunity to determine the kind of pathogen and viral load.
- Digene-test – high-precision identification of DNA oncogenic strains of the hpv virus. The study serves as a reliable screening.
Treatment treatment
Developed drugs against HPV infection allow you to just remove the symptoms of the disease and prevent malignancy tissue. Complete removal of the virus with the help of medical therapy is not possible. Oral and topical remedies are intended in the case of a high risk of oncogenesis, immunodeficiency, and other adverse conditions. If the virus manifests itself to external changes, it is quite common preventive measures.
Possible destinations
- Salicylic acid for wart removal. No is used for processing the skin of the face and genitals.
- Creams and ointments that contain immunomodulatory agents.
- Podofilox – ointment, which has cytotoxic action. Applying the medication to the affected skin leads to the destruction of pathogenic elements.
- Trichloroacetic acid for chemical cautery of common and genital warts. May cause local partition expression.
Mentioned medications should only be used under medical control. After removal of warts HPV infection may manifest itself again, and even expand to other areas.
Surgical treatment
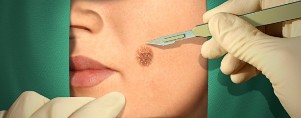
The physician may offer the patient surgical and minimally invasive ways to remove warts. Typically, these methods do not cause complications, however, in the first days after the procedure may occur bleeding of the tissues.
Types of interventions:
- common surgical excision;
- freezing with liquid nitrogen, with subsequent destruction of the affected tissue;
- electric coagulation;
- removal of papillomas with a laser.;
- the use of radio waves "knives".
All treatments are carried out in local anesthesia. The specialist will choose the safest method of treatment of warts.
Weather
During papilomyaviruses infection depends on the immune status of the patient and the particular strain of the virus. About 30% of the population arises from a spontaneous removal of the causative agent of the disease, the conditioned active immunity. Symptomatically the disease often manifests in pregnant women, children, the elderly and patients with immunodeficiency.
For HPV-infection is a typical recurrent time. These body parts of the papilloma may gradually disappear or spread to adjacent areas of the skin. Oncogenic strains of the virus most often affects the mucosa of the cervical canal, and which originated epithelial dysplasia increases the effect of the risk factors of malignant tissue degeneration, such as smoking and use of hormonal contraceptives. The tumor may form over the 10-20 years after the assault of the virus into the body.
Prevention
The most reliable method of prevention is timely vaccination. Vaccine "Gardasil", containing viral proteins and auxiliary components, is effective against HPV 6, 11, 16 and 18 types. If vaccination is carried out at an early age of first sexual intercourse, the risk of later development of cervical cancer in women, is not greater than 1%.
Another prevention is:
- the use of condoms;
- sexual connection only with verified partners;
- thorough personal hygiene;
- gynecological examination at least once a year.























